 DEFINITION
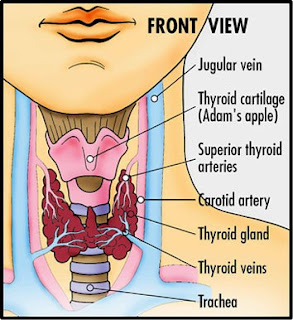
DEFINITION Hurthle cell cancer is a rare type of cancer that attacks the thyroid gland, a gland located in front of the neck down. The thyroid secretes hormones that are important to regulate the body's metabolism. Hurthle cell cancer can be aggressive and surgery is usually performed to remove the thyroid gland that has cancer.
Among the new cases of thyroid cancer, less than 5 percent are Hurthle cell cancers. The disease is also called Hurthle cell carcinoma, or sometimes called oxyphil cell carcinoma.
SYMPTOMS
Signs and symptoms of hurthle cell cancer include:
• The lump is rapidly growing, slightly below the adam's apple.
• Pain in the neck and throat with ear pain that sometimes occurs.
• Hoarseness or voice change.
• Shortness of breath.
• It is hard to swallow.
• A cough that is caused by respiratory tract infections.
Causes & Risk Factors
Cause
The precise cause is unknown hurthle cell cancer, although scientists believe the condition is associated with changes in DNA, including the relationship with the aging process.
In general, cancer begins when a mutation occurs in the cell DNA. DNA mutations can cause cells to function normally. The mutation causes the cells to grow out of control and later life when other cells die. Accumulation of cells that form tumors can spread to other body areas.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk hurthle cell cancer include:
• Women
• Old age
• Treatment of radiation to the head and neck
Prevention
You can reduce the risk hurthle cell cancer by reducing exposure to radiation from X-rays or other sources.